PVC CONDUIT
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
How To Order PVC Conduit From Central Conduit
The easiest way to get a quote or place an order is to use the Request a Quote page.
To speak with a human, call us. Someone will pickup the phone.
How Central Conduit Supplies To You
Although, schedule 40 is the most popular item, Central Conduit sells PVC conduit in all sizes, all lengths, and all schedules.
That means that if you need Schedule 40, Schedule 80, TC-6 DB-60, TC-8 DB-120, TC-8 EB-35, DB 100, Type C (White or Gray) or Gas Sleeve conduit, Central Conduit can supply that for you.
Your order is placed directly with a major US manufacturer of conduit such as JM Eagle or Atkore and shipped directly to your job site. This eliminates one trip to a warehouse or distributors’ yard, ultimately reducing your conduit expense.
Every piece of conduit Central Conduit supplies is Made in the USA and is certified to UL 651 and NEMA TC2 standards. This means that our product is approved for your project, including all government and DOT projects.
To learn more about PVC conduit and that Central Conduit supplies, keep reading.
What is PVC Conduit?
PVC conduit, short for polyvinyl chloride conduit, is a rigid, non-metallic piping system designed to protect and route electrical and communications wiring. It is lightweight, non-conductive, corrosion-resistant, and manufactured to UL 651 and NEMA TC-2 standards, ensuring full code compliance across industries.
PVC conduit is produced in several standardized types. The most common are Schedule 40 and Schedule 80, which differ in wall thickness and strength. Other specialized types, such as Type EB (Encased Burial) and Type A (Direct Burial), are used in large utility and communications projects. We’ll cover each of these in more detail later in this guide.
Unlike metal conduit, PVC will not rust or corrode in soil or moisture-rich environments, making it the industry standard for underground installations.
Standards and Compliance
PVC conduit is manufactured to UL 651 and NEMA TC-2 standards, ensuring full compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC Article 352). These certifications confirm that every length of conduit meets strict requirements for safety, performance, and long-term reliability.
Durability and Safety
When properly installed, PVC conduit can last for decades underground without rust, corrosion, or degradation. Its non-conductive design reduces electrical fault risks and improves job site safety, while its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and soil conditions makes it a dependable low-maintenance solution.
Why PVC Conduit?
Lightweight
Easy install
Non-Conductive
Extra Safety
Corrosion Resistant
No rust
Cost-Effective
Lower costs
Durable
Long life
Availability
Always in Stock
What are the Key Advantages of PVC Conduit?
PVC conduit is more than just a code requirement — it’s a practical choice that helps contractors and project managers deliver work on time and within budget. Its combination of safety, durability, and ease of installation makes it the go-to option for projects of every size. The most important advantages include:
- Lightweight and easy to install — cuts labor time compared to metallic conduit.
- Non-conductive — adds an extra layer of safety for electrical systems.
- Corrosion and chemical resistant — ideal for damp soil and harsh environments.
- Cost-effective — lower material and installation costs than steel alternatives.
- Durable and long-lasting — maintains performance across decades of use.
- Wide availability — PVC conduit is stocked nationwide in all trade sizes, making it easy to source on tight project schedules.
- Standardized fittings and compatibility — couplings, elbows, and bends are universally available and interchangeable.
- Versatile installation options — approved for direct burial, encasement in concrete, or above-ground applications (per NEC Article 352).
- Weather and UV resistance — sunlight-resistant formulations are available for outdoor exposure.

Where is PVC Conduit used?
PVC conduit is the industry standard for underground electrical and communication wiring. Whenever power or data needs to run safely below ground, contractors turn to PVC conduit. Its durability, code compliance, and cost-effectiveness make it the default choice across industries, including:
- Electrical Power Distribution — the most common application, PVC conduit is specified for residential neighborhoods, commercial buildings, and large-scale industrial facilities.
- Telecommunications and Fiber Optic Networks — It protects fiber optic cables in data centers, broadband systems, and 5G networks.
- Roadway and Transportation Projects — Highways, airports, and traffic systems use PVC conduit for underground lighting and control wiring.
- Energy and Power Generation Facilities — Substations, solar farms, wind farms, gas plants, and nuclear plants all specify PVC conduit.
- Municipal and Utility Infrastructure — Water treatment plants, pump stations, and public utility networks rely on PVC conduit for underground wiring.
- Military and Federal Facilities — Bases, defense installations, and mission-critical communications use PVC conduit for durability and compliance.
- State and Local Government Projects — Schools, universities, hospitals, and courthouses all use PVC conduit for safe power and data distribution.
- Large-Scale Construction Projects — EPCs and contractors specify PVC conduit on data centers, mega-solar projects, and other major builds.
Beyond its everyday uses and advantages, PVC conduit is also governed by strict industry standards such as UL 651, NEMA TC-2, and the National Electrical Code (NEC), which ensure safety, consistency, and full code compliance.
Standards and Compliance for PVC Conduit
PVC conduit is required to meet strict industry standards that guarantee safety, performance, and code compliance. The three primary frameworks are UL 651, NEMA TC-2, and the National Electrical Code (NEC Article 352). In addition, many projects require third-party testing and certification from organizations such as ETL or CSA. Together, these standards ensure conduit performs reliably in every application, from residential wiring to large-scale utility projects.
What does UL 651 Cover?
Underwriter Laboratories developed UL 651 as the governing standard for rigid PVC conduit and fittings. It applies to Schedule 40, Schedule 80, Type EB, and Type A conduit, and defines the requirements for material composition, wall thickness, inside and outside diameters, crush and impact strength, UV resistance, flame resistance, and permanent markings for compliance and traceability.

Key Requirements of UL 651
- Dimensional Accuracy – tightly controlled outside diameter, inside diameter, and wall thickness for each trade size.
- Performance Testing – conduit must pass crush resistance, impact resistance, sunlight (UV) exposure, and flammability tests.
- Material Quality – conduit must be made from virgin PVC resin with specific density and tensile strength.
- Marking & Traceability – every stick of conduit must carry permanent markings showing schedule, trade size, UL listing, and manufacturer.
What is NEMA TC-2?
According to National Electrical Manufacturers Association, NEMA TC-2 is the standard for electrical PVC conduit types EPC-40 (Schedule 40) and EPC-80 (Schedule 80). It establishes the dimensional, material, and performance requirements for conduit—including outside and inside diameters, wall thickness, impact resistance, and long-term durability—and ensures consistent quality across all manufacturers.

Key Requirements of NEMA TC-2
- Dimensional Standards – establishes exact outside diameters, inside diameters, and wall thickness for Schedule 40 and 80 conduit.
- Material Specifications – requires rigid PVC formulated for electrical use, with consistent density and tensile properties.
- Mechanical Performance – sets benchmarks for crush strength and impact resistance to ensure conduit can withstand job site conditions.
- Application Classification – identifies conduit for normal-duty and heavy-duty service in above ground, concrete-encased, and direct-burial installations.
NEMA TC-2 is almost always referenced alongside UL 651 because both standards are required for Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 conduit. While NEMA TC-2 focuses on dimensional accuracy and material consistency, UL 651 governs testing, safety, and performance validation. When conduit is marked with both standards, it assures contractors, inspectors, and engineers that the product meets the full set of requirements for code compliance and field reliability.
What does NEC Article 352 cover for PVC conduit?
According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), Article 352 governs rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) conduit. It specifies where PVC conduit can be installed, burial depth and support requirements, temperature and fire limitations, and rules for fittings and joints—ensuring installations are safe and code-compliant across all applications.

Key Requirements of NEC Article 352
- Permitted Uses – allows PVC conduit in underground, concealed, and exposed installations when properly supported and protected.
- Temperature Ratings – defines maximum operating temperatures (typically 90°C conductors) and restrictions near high-heat sources.
- Fire Resistance – prohibits PVC conduit in certain plenum spaces unless tested and rated for flame spread.
- Burial Depths – sets minimum cover requirements depending on location (driveways, sidewalks, roadways, open ground).
- Support & Securement – requires conduit to be strapped, clamped, or otherwise supported at defined intervals.
- Fittings & Joints – mandates use of listed fittings, solvent-welded joints, and proper transitions to other raceway types.
Who tests PVC conduit besides UL?
There are many testing agencies around the world. In the US and Canada the most popular are Intertek/ETL, and CSA. These are all OSHA recognized laboratories that apply the same safety requirements. While UL is the most familiar name, ETL and CSA certifications are equally valid and code-compliant. Regardless of which mark appears, all indicate that the product has been independently tested to the full requirements of UL 651.

Key Requirements of ETL and CSA
- Compliance with UL 651 – conduit must meet all dimensional, material, and performance requirements defined in UL 651.
- Independent Verification – ETL and CSA conduct their own testing rather than relying on UL’s labs.
- Ongoing Factory Audits – inspectors perform regular factory inspections to verify continued compliance.
- Marking & Traceability – products certified by ETL must carry the ETL Listed mark with identifying codes for traceability. Same for CSA.
- Recognition by OSHA & AHJs – ETL is recognized as an NRTL in the U.S., meaning its certification is accepted by inspectors, building authorities, and codes just like UL.
PVC Conduit Frequently Asked Questions
Types of PVC Conduit
PVC electrical conduit is manufactured in several wall thicknesses and designations to meet the requirements of different environments and installation methods. The two primary categories are Schedule 40 and Schedule 80, both defined under UL 651 and NEMA TC-2, with additional classifications such as EB (Encased Burial) and DB (Direct Burial) for utility and infrastructure applications.
Each type of PVC conduit is engineered to balance strength, weight, and cost for specific use cases — from residential and commercial wiring runs to industrial plants, substations, data centers, and nationwide utility projects. Understanding these classifications is essential for engineers, project managers, and contractors to ensure proper code compliance, mechanical protection, and long-term system reliability.
Choosing the correct PVC conduit type at the design stage is critical — the wrong specification can lead to failed inspections, costly rework, or premature system failure.
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
Schedule 40 PVC conduit is the most widely specified nonmetallic raceway in the electrical industry. Recognized by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and manufactured under UL 651 and NEMA TC-2, it is designed to provide mechanical protection for conductors in a wide range of environments while remaining lightweight, easy to install, and cost-effective.
Engineering Profile
- Wall Thickness: Standard-wall design, balancing durability with material efficiency.
- Inside Surface: Smooth, low-friction bore that reduces conductor pulling tension and minimizes jacket damage.
- Material Properties: Rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) compound meeting ASTM D1784 requirements for impact strength, tensile strength, and flammability.
- Temperature Rating: Suitable for use up to 90°C conductors, per NEC guidelines, if so marked by the manufacturer.
- Non-conductive: Inherently dielectric, eliminating the need for supplemental coatings or corrosion protection.
Primary Applications
- Residential and Commercial: Feeder conduits, risers, branch circuits, and service entrances.
- Utility and Infrastructure: Underground distribution, solar arrays, telecom, and duct banks.
- Industrial: Non-hazardous plant areas where heavy mechanical abuse is not expected.
Advantages
- Lower material cost compared to Schedule 80 or steel conduit.
- Widely available at distributors, home improvement stores, and factories, keeping prices competitive.
- Reduced labor cost thanks to lighter weight and easier handling.
- Solvent welding quick joining method with PVC cement — no threading, welding, or heavy equipment required.
- Compatibility with standardized fittings and couplings make it easy to connect long runs.
Limitations
- Not suitable where high mechanical abuse or crush resistance is expected (road crossings, exposed industrial runs).
- Lower impact resistance than Schedule 80.
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit – Trade Sizes and Technical Specifications
| Part Number | Trade Size | Schedule | Pipe Length (ft) | Wall Thickness (in( | Outside Diameter (O.D.) | Inside Diameter (I.D.) | Total Feet per Crate | Weight per 100 ft | Total Crate Weight (lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 504010 | 1/2 | 40 | 10 | 0.109 | 0.84 | 0.622 | 6,000 | 17 | 1020 |
| 754010 | 3/4 | 40 | 10 | 0.113 | 1.05 | 0.824 | 4,400 | 22 | 968 |
| 1004010 | 1 | 40 | 10 | 0.133 | 1.315 | 1.049 | 3,600 | 33 | 1172 |
| 1254010 | 1-1/4 | 40 | 10 | 0.140 | 1.66 | 1.38 | 3,300 | 44 | 1452 |
| 1504010 | 1-1/2 | 40 | 10 | 0.145 | 1.9 | 1.61 | 2,250 | 53 | 1186 |
| 2004010 | 2 | 40 | 10 | 0.154 | 2.375 | 2.067 | 1,400 | 73 | 1022 |
| 2504010 | 2-1/2 | 40 | 10 | 0.203 | 2.875 | 2.469 | 930 | 116 | 1079 |
| 3004010 | 3 | 40 | 10 | 0.216 | 3.5 | 3.068 | 880 | 161 | 1417 |
| 3504010 | 3-1/2 | 40 | 10 | 0.226 | 4 | 3.548 | 630 | 194 | 1222 |
| 4004010 | 4 | 40 | 10 | 0.237 | 4.5 | 4.026 | 570 | 229 | 1305 |
| 5004010 | 5 | 40 | 10 | 0.258 | 5.563 | 5.047 | 380 | 311 | 1182 |
| 6004010 | 6 | 40 | 10 | 0.280 | 6.625 | 6.065 | 260 | 403 | 1045 |
| 8004010 | 8 | 40 | 10 | 0.332 | 8.625 | 7.942 | 140 | 607 | 850 |
| 504020 | 1/2 | 40 | 20 | 0.109 | 0.84 | 0.622 | 12,000 | 17 | 1980 |
| 754020 | 3/4 | 40 | 20 | 0.113 | 1.05 | 0.824 | 8,800 | 22 | 1936 |
| 1004020 | 1 | 40 | 20 | 0.133 | 1.315 | 1.049 | 7,200 | 33 | 2376 |
| 1254020 | 1-1/4 | 40 | 20 | 0.140 | 1.66 | 1.38 | 6,600 | 44 | 2904 |
| 1504020 | 1-1/2 | 40 | 20 | 0.145 | 1.9 | 1.61 | 4,500 | 53 | 2375 |
| 2004020 | 2 | 40 | 20 | 0.154 | 2.375 | 2.067 | 2,800 | 73 | 2044 |
| 2504020 | 2-1/2 | 40 | 20 | 0.203 | 2.875 | 2.469 | 1,860 | 116 | 2158 |
| 3004020 | 3 | 40 | 20 | 0.216 | 3.5 | 3.068 | 1,760 | 161 | 2834 |
| 3504020 | 3-1/2 | 40 | 20 | 0.226 | 4 | 3.548 | 1,260 | 194 | 2435 |
| 4004020 | 4 | 40 | 20 | 0.237 | 4.5 | 4.026 | 1,140 | 229 | 2612 |
| 5004020 | 5 | 40 | 20 | 0.258 | 5.563 | 5.047 | 760 | 311 | 2364 |
| 6004020 | 6 | 40 | 20 | 0.280 | 6.625 | 6.065 | 520 | 403 | 2096 |
| 8004020 | 8 | 40 | 20 | 0.332 | 8.625 | 7.942 | 280 | 607 | 1700 |
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is manufactured with a thicker wall than Schedule 40, providing greater mechanical protection for conductors in environments subject to impact, crush loads, or frequent exposure. Like Schedule 40, it is governed by UL 651 and NEMA TC-2, but its heavier construction makes it the preferred choice in industrial plants, substations, road crossings, and other high-risk installations.
Engineering Profile
- Wall Thickness: Between 34% and 54% thicker than Schedule 40 of the same trade size. (See chart below)
- Mechanical Properties: Higher tensile strength, crush resistance, and impact durability.
- Inside Surface: Smooth, low-friction bore that reduces conductor pulling tension and minimizes jacket damage.
- Material Properties: Rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) compound meeting ASTM D1784 requirements for impact strength, tensile strength, and flammability.
- Temperature Rating: Suitable for use up to 90°C conductors, per NEC guidelines, if so marked by the manufacturer.
- Non-conductive: Inherently dielectric, eliminating the need for supplemental coatings or corrosion protection.
Primary Applications
- Exposed runs where conduit is subject to mechanical damage.
- Road and highway crossings (direct burial under vehicle traffic).
- Utility substations and industrial facilities.
- Vertical risers in warehouses, factories, or utility yards.
- Anywhere specified by engineering.
Advantages
- Superior protection in high-risk areas.
- Long service life even in exposed conditions.
- NEC-approved for direct burial, concrete encasement, and aboveground use.
- Solvent welding quick joining method with PVC cement — no threading, welding, or heavy equipment required.
- Compatibility with standardized fittings and couplings make it easy to connect long runs.
Limitations
- Heavier weight → higher handling cost compared to Schedule 40.
- Slightly higher material cost.
- Over-specifying can add unnecessary cost if mechanical protection is not required.
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit – Trade Sizes and Technical Specifications
| Part Number | Trade Size | Schedule | Pipe Length (ft) | Wall Thickness (in) | Outside Diameter (O.D.) | Inside Diameter (I.D.) | Total Feet per Crate | Weight per 100 ft | Total Crate Weight (lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 508010 | 1/2 | 80 | 10 | 0.147 | 0.84 | 0.546 | 6,000 | 22 | 1320 |
| 758010 | 3/4 | 80 | 10 | 0.154 | 1.05 | 0.742 | 4,400 | 30 | 1320 |
| 1008010 | 1 | 80 | 10 | 0.179 | 1.315 | 0.957 | 3,600 | 42 | 1512 |
| 1258010 | 1-1/4 | 80 | 10 | 0.191 | 1.66 | 1.278 | 3,300 | 60 | 1980 |
| 1508010 | 1-1/2 | 80 | 10 | 0.200 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 2,250 | 72 | 1620 |
| 2008010 | 2 | 80 | 10 | 0.218 | 2.375 | 1.939 | 1,400 | 98 | 1372 |
| 2508010 | 2-1/2 | 80 | 10 | 0.276 | 2.875 | 2.323 | 930 | 160 | 1488 |
| 3008010 | 3 | 80 | 10 | 0.300 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 880 | 213 | 1874 |
| 3508010 | 3-1/2 | 80 | 10 | 0.318 | 4 | 3.365 | 630 | 255 | 1607 |
| 4008010 | 4 | 80 | 10 | 0.337 | 4.5 | 3.826 | 570 | 309 | 1761 |
| 5008010 | 5 | 80 | 10 | 0.375 | 5.563 | 4.813 | 380 | 430 | 1634 |
| 6008010 | 6 | 80 | 10 | 0.432 | 6.625 | 5.76 | 260 | 589 | 1531 |
| 508020 | 1/2 | 80 | 20 | 0.147 | 0.84 | 0.546 | 12,000 | 22 | 2640 |
| 758020 | 3/4 | 80 | 20 | 0.154 | 1.05 | 0.742 | 8,800 | 30 | 2640 |
| 1008020 | 1 | 80 | 20 | 0.179 | 1.315 | 0.957 | 7,200 | 42 | 3024 |
| 1258020 | 1-1/4 | 80 | 20 | 0.191 | 1.66 | 1.278 | 6,600 | 60 | 3960 |
| 1508020 | 1-1/2 | 80 | 20 | 0.200 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 4,500 | 72 | 3240 |
| 2008020 | 2 | 80 | 20 | 0.218 | 2.375 | 1.939 | 2,800 | 98 | 2744 |
| 2508020 | 2-1/2 | 80 | 20 | 0.276 | 2.875 | 2.323 | 1,860 | 160 | 2976 |
| 3008020 | 3 | 80 | 20 | 0.300 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 1,760 | 213 | 3749 |
| 3508020 | 3-1/2 | 80 | 20 | 0.318 | 4 | 3.365 | 1,260 | 255 | 3213 |
| 4008020 | 4 | 80 | 20 | 0.337 | 4.5 | 3.826 | 1,140 | 309 | 3523 |
| 5008020 | 5 | 80 | 20 | 0.375 | 5.563 | 4.813 | 760 | 430 | 3268 |
| 6008020 | 6 | 80 | 20 | 0.432 | 6.625 | 5.76 | 520 | 589 | 3063 |
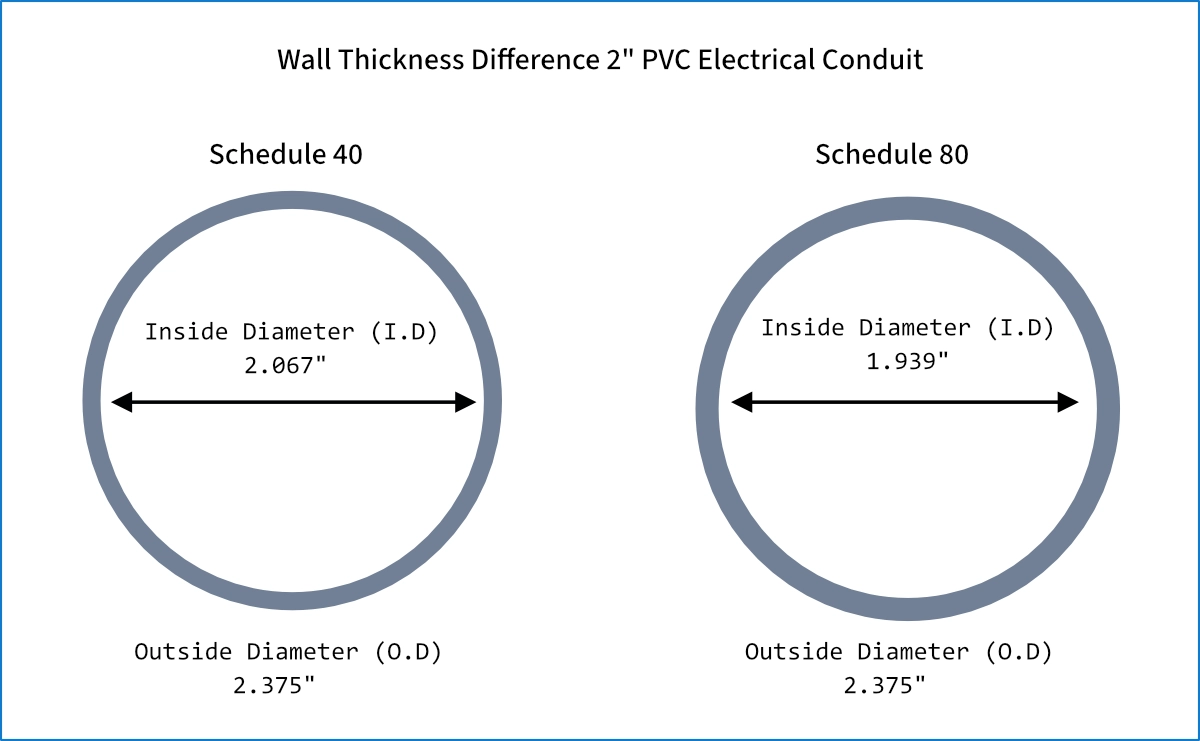
Wall Thickness & Fill
Schedule 80 PVC conduit has a thicker wall than Schedule 40, but the OD is unchanged to keep fittings and knockouts compatible. The extra wall thickness comes from the inside, reducing the ID and usable cross-sectional area, so conductor fill capacity is lower than Schedule 40 at the same trade size. Use NEC Chapter 9, Table 4 for the Schedule 80 values when calculating fill.
Wall Thickness Table – Schedule 40 and Schedule 80
| Trade Size | Outside Diameter (O.D) | Wall Thickness (in) Sch 40 | Wall Thickness (in) Sch 80 | % Thicker | Inside Diameter (in) Sch 40 | Cross-Sectional Area (sq in) – Sch 40 | Inside Diameter (in) Sch 80 | Cross-Sectional Area (sq in) – Sch 80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 0.84 | 0.109 | 0.147 | 34.9 | 0.622 | 0.304 | 0.546 | 0.234 |
| 3/4 | 1.05 | 0.113 | 0.154 | 36.3 | 0.824 | 0.533 | 0.742 | 0.432 |
| 1 | 1.315 | 0.133 | 0.179 | 34.6 | 1.029 | 0.832 | 0.957 | 0.719 |
| 1-1/4 | 1.66 | 0.140 | 0.191 | 36.4 | 1.360 | 1.453 | 1.278 | 1.282 |
| 1-1/2 | 1.9 | 0.145 | 0.200 | 37.9 | 1.610 | 2.035 | 1.500 | 1.767 |
| 2 | 2.375 | 0.154 | 0.218 | 41.6 | 2.047 | 3.291 | 1.939 | 2.953 |
| 2-1/2 | 2.875 | 0.203 | 0.276 | 36.0 | 2.445 | 4.694 | 2.323 | 4.236 |
| 3 | 3.5 | 0.216 | 0.300 | 38.9 | 3.042 | 7.268 | 2.900 | 6.601 |
| 3-1/2 | 4 | 0.226 | 0.318 | 40.7 | 3.500 | 9.5621 | 3.356 | 8.845 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 0.237 | 0.337 | 42.2 | 4.026 | 12.730 | 3.826 | 11.497 |
| 5 | 5.563 | 0.258 | 0.375 | 45.3 | 5.047 | 19.990 | 4.768 | 17.848 |
| 6 | 6.625 | 0.280 | 0.432 | 54.3 | 6.065 | 28.903 | 5.761 | 26.063 |
| 8 | 8.625 | 0.332 | Not Manufactured | Not Applicable | 7.942 | 49.535 | Not Applicable | Not Applicable |

Need PVC Conduit for Your Next Project?
Request a Quote Today for Fast, Reliable Delivery
on Schedule 40 PVC Conduit

Built for Tough Jobs – Choose Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
Engineered for Heavy-Duty Applications.
Request a Quote Today.